Getting Started with Full Stack
Course Introduction
Slides
Part 1
Things you’ll learn
- Learn how to use Node and Bash to create shell scripts
- Learn advanced Nginx configuration
- Common server vulnerabilibies and how to mitigate them
- How to add HTTPS to your server
- Understand databases
- Containers and automating deployments
Full Stack for Frontend Part 1 Recap & Purpose
Recap
- How the internet works
- Command line basics
- How to create and manage a web server
- Create a deploy system for a Node app
- Build a basic web page
Why full stack
emm.. a lot of reasons…
Server Setup
Basic Server Setup, Updating and User Permissions
- Create a new Ubuntu server
a. Use Ubuntu 16.04.x
b. Be sure to use an SSH key
- Point domain to new server
- Log into server as root
- Update server
- Add a new user ‘test’
- Grant ‘test’ sudo access
- Switch to ‘test’ user
Node setup and installation
update apt repo for nodejs
1
| curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_6.x | sudo -E bash -
|
explain shell
install nodejs and npm
check npm directory
If the npm directory is not /usr/local, follow instructions here.
更改npm安装目录主要是权限问题。如果安装在全局文件夹下,需要sudo权限才能安装全局包。
install forever module
change working directory
更改文件夹权限
1
| sudo chown -R $USER:$USER /var/www
|
clone repo
1
| git clone https://github.com/young/fsfe2.git
|
change working directory again
install module
Server Security
Security Overview
- Control access
- Strong authentication
- Firewalls
- user/file permissions
- Secure your applications
- Keep software up to date
- limit application use
Adding SSH keys
create a new directory
paste public key into authorized_keys file
1
| vi ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
|
Be sure to test logging in with your new user.
Security Setting
- Add a password for root
- Disable root login
- Disable password login
Firewalls
nmap
Firewall configurations: iptables
1
| sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
|
-A append rule-p protocol(tcp, icmp)--dport destination port-j jump(DROP, REJECT, ACCEPT, LOG)
Create an iptable rule to block all outgoing HTTP connections
1
| iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j REJECT
|
Create an iptable rule to only allow icmp connections on port 892 from the IP address 192.0.0.1
1
| iptables -A INPUT -s 192.0.0.1 -p icmp --dport 892 -j ACCEPT
|
Firewall configurations: UFW and GUI options
There has to be a better way!
ufw - uncomplicated firewall
1
2
| sudo ufw allow ssh
sudo ufw enable
|
Create a ufw rule to block all outgoing HTTP connections
GUI
Degital Ocean的Droplets下的networking下的firewalls选项
Automatic Updates
1
| sudo apt install unattended-upgrades
|
/etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades
1
2
| APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists "1";
APT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade "1";
|
https://wiki.debian.org/UnattendedUpgrades
1
| sudo vi /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/50unattended-upgrades
|
Fail2ban: Exercise
Install fail2ban
1
| sudo apt install fail2ban
|
Copy jail file
1
| sudo cp /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
|
Edit configuration file
1
| sudo vi /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
|
WARNING!
If you misconfigure fail2ban, you can lock yourself out of your server!
Advanced Shells
- Finding Things
- Redirection Operators
- Shells
- Shell Scripts
find: search file names
find |
/bar |
-name |
foo.txt |
| find |
directory |
option |
file/folder |
useful options
- -name
- -type
- -empty
- -executable
- -writable
grep: search file contents
grep |
-i |
'jem' |
/var/www |
| grep |
options |
search expression |
directory |
search inside gzip file
Find: Exercise
find all log files in /log
1
| find /var/log/ -type f -name *.log
|
find all empty files
1
| find /etc -type f -empty
|
find all directories with the word log
1
| find / -type d -name log
|
Grep: Exercise
Redirection
write to file
Shells
shell => application => kernel
show current shell:
Changing Shells
list acceptable shells to change to
change shell to sh
login into new shell to see the change
change shell to bash
Shell scripting
Why shell scripting ?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| #!/bin/sh
trap 'echo "/nPlease choose!"' INT
FILES= `find /var/log/ -name *.log -mtime 1`
echo "Old files ready to be deleted:\n"
echo "$FILES"
echo "Do you want to continue? \c"
while :
do
read INPUT
case $INPUT in
y)
echo "deleting files..."
break
;;
*)
echo "Please make a valid selection"
;;
esac
done
|
Bash scripting: Exercise
1
2
3
| #!/bin/sh
cat /proc/loadavg | awk '{print $1"-"$2"-"$3}'
|
Get load average:
Extract the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd columns of data:
1
| awk '{print $1"-"$2"-"$3}'
|
Make executable:
1
| sudo chmod 755 ./load.sh
|
Creating a shell script with Node: Exercise
create a workspace folder:
move into workspace folder:
create index.js:
initialize project:
add reference to script:
1
2
3
| "bin": {
"myscript": "index.js"
},
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| #!/user/bin/node
const exec = require('child_process').exec
const stat = exec(`cat /proc/loadavg | awk '{print $1"-"$2"-"$3}'`)
stat.stdout.on('data', function(data) {
console.log(data)
})
|
HTTPS
- Nginx setup
- Why HTTPS
- Getting a certificate
- Cron
Nginx Setup: Installation
- Install nginx
sudo apt-get install nginxsudo service ngnix start
- Proxy traffic to node server
- Add domain name
- Open port 443
- Reload nginx
Nginx Setup: proxy traffic to node server
1
| cd /etc/ngnix/site/available
|
1
2
3
| location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3001/;
}
|
测试配置文件是否有效:
1
2
3
4
| sudo nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
|
启动forever是提示command not found,查了一下是全局变量配置问题,使用如下命令修改配置
1
| sudo echo -e "export PATH=$(npm prefix -g)/bin:$PATH" >> ~/.bashrc && source ~/.bashrc
|
此时打开网址,可以看到已经显示站点。
Nginx Setup: Adding a domain name and opening port 443
add domain name to nginx conf
1
| sudo vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
|
1
| server_name $YOUR_DOMAIN;
|
open port 443:
open ssh link
enable ufw
check ufw status
Why HTTPS
简单来说,HTTPS更加安全,是一种必要措施。
- Security
- Technology
- Service Workers
- Web Bluetooth
- HTTP/2
Installing HTTPS certificate
Old way:
acme-tiny
New way:
certbot
- Add the certbot repository
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:certbot/certbot
- Pull in new repository information
- Install certbot with nginx plugin
sudo apt install python-certbot-nginx
- Use certbot to get certificate
- Test auto renew
sudo certbot renew --dry-run
安装时开始一直失败,输入sudo ufw disable,把防火墙暂时关闭后安装成功。
此时在通过域名访问网站即可发现https已经启用。
cron
How do we run periodic tasks?
| minute |
hour |
day of month |
month |
day of week |
command to execute |
00 |
16 |
* |
* |
5 |
`echo “It’s party time!” |
crontab-The quick and simple editor for cron schedule expressions
cron: Exercise
Open crontab for editing
Renew certificate every week at 12pm on Monday
1
| 00 12 * * 1 certbot renew
|
Nginx Tuning
Nginx Tuning: Overview and Gzip
gzip is an algorithm that runs through and compresses files
1
| sudo vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
|
1
| sudo vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
|
添加如下规则:
1
2
3
4
| location /static/ {
expires 30d;
proxy_padd http://127.0.0.1:3001/static/;
}
|
测试规则
重启Nginx,刷新网页,会在Response Headers的Cache-Control中看到max-age=2592000。
当缓存时间设置比较长时,网站更新后并不会在客户端更新。
Caching
上述是客户端缓存设置,也可以对服务端进行缓存设置,来使得一些复杂的sql语句查询或者一些大计算量的请求进行缓存,提高访问速度(缓存时间不宜过长,否则无法进行更新)。
1
| sudo vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
|
文件头部添加(server{}外)
1
2
3
4
5
| proxy_cache_path /tmp/nginx levels=1:2
keys_zone=slowfile_cache:10m inactive=60m
use_temp_path=off;
proxy_cache_key "$request_uri";
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| location /slowfile {
proxy_cache_valid 1m;
Proxy_ignore_headers Cache-Control;
add_header X-Proxy-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
proxy_cache slowfile_cache;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3001/slowfile;
}
|
warm cache:对一些耗时较长的请求首先进行缓存,这样在他人访问时可以直接从缓存中获取,提高访问速度。
此时访问网站的/slowfile,第一次访问可以看到请求头添加了X-Proxy-Cache字段,并且为MISS,请求时间较长。刷新后X-Proxy-Cache字段为HIT,请求仅耗时300ms。
Websockets: Setup
1
| sudo vi /etc/nginx/sites-avaliable/default
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| location / {
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3001;
}
|
通过上述配置,Nginx开启Websockets。
Websockets: Client-side code and observables
Websockets: Exercise
1
2
3
| cd /var/www/fsfe2/
vi app.js
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| function getServerLoad() {
return setInterval(() => {
const loadScript = exec(`~/load.sh`);
loadScript.stdout.on('data', function(data) {
wss.broadcast(JSON.stringify({name: 'load', data}));
});
}, 2 * 1000);
}
|
http/2
1
| sudo vi /etc/nginx/sites-avaliable/default
|
demo
http/2: Exercise
更改配置文件后,重启Nginx,打开/cats网址,会看到图片传输协议已经更改为h2
Redirect
Redirect request to new url
1
| sudo vi /ect/nginx/sites-avaliable/default
|
1
2
3
| location /help {
return 301 https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/;
}
|
Databases
Database Types
- relational
- SQL
- MySQL
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Postgre SQL
- non-relational
Exercise: MySQL Installation
Install MySQL
1
| sudo apt install mysql-server
|
Run setup script
1
| mysql_secure_installation
|
Login as root
Database Best Practice
Tips:
- Back up your database
- Use a strong root password
- Don’t expose the database outside the network
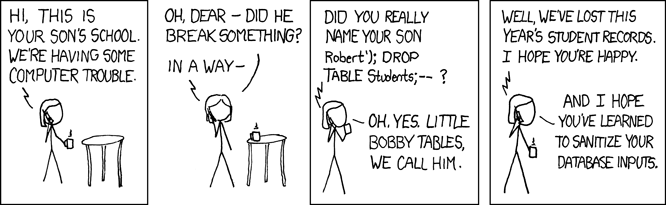
- Sanitize your SQL
- Back up your database
Containers and More
Containers
- shared resources
- no OS
- fast deployment
Docker-Enterprise Container Platform for High-Velocity Innovation
Installing Postgres on Docker
Orchestration
Tools
Kubernetes
Automated Deployment
